|
|
最近时间少了, 隔了这么久, 才做了一个网站 |

概 述
在前文《基于Spring Security和 JWT的权限系统设计》之中已经讨论过基于 Spring Security和 JWT的权限系统用法和实践,本文则进一步实践一下基于 Spring Security Oauth2实现的多系统单点登录(SSO)和 JWT权限控制功能,毕竟这个需求也还是蛮普遍的。
代码已开源,放在文尾,需要自取
理论知识
在此之前需要学习和了解一些前置知识包括:
- Spring Security:基于
Spring实现的Web系统的认证和权限模块 - OAuth2:一个关于授权(
authorization)的开放网络标准 - 单点登录 (SSO):在多个应用系统中,用户只需要登录一次就可以访问所有相互信任的应用系统
- JWT:在网络应用间传递信息的一种基于
JSON的开放标准((RFC 7519),用于作为JSON对象在不同系统之间进行安全地信息传输。主要使用场景一般是用来在 身份提供者和服务提供者间传递被认证的用户身份信息
要完成的目标
- 目标1:设计并实现一个第三方授权中心服务(
Server),用于完成用户登录,认证和权限处理 - 目标2:可以在授权中心下挂载任意多个客户端应用(
Client) - 目标3:当用户访问客户端应用的安全页面时,会重定向到授权中心进行身份验证,认证完成后方可访问客户端应用的服务,且多个客户端应用只需要登录一次即可(谓之 “单点登录
SSO”)
基于此目标驱动,本文设计三个独立服务,分别是:
- 一个授权服务中心(codesheep-server)
- 客户端应用1(codesheep-client1)
- 客户端应用2(codesheep-client2)
多模块(Multi-Module)项目搭建
三个应用通过一个多模块的 Maven项目进行组织,其中项目父 pom中需要加入相关依赖如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.0.8.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.spring.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>platform-bom</artifactId>
<version>Cairo-RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Finchley.SR2</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>项目结构如下:
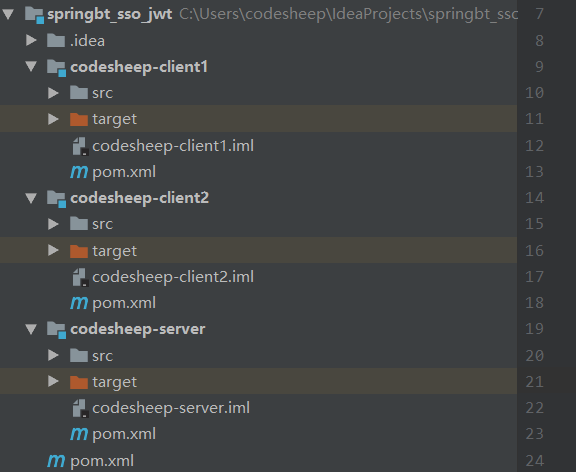
授权认证中心搭建
授权认证中心本质就是一个 Spring Boot应用,因此需要完成几个大步骤:
pom中添加依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-oauth2</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>- 项目
yml配置文件:
server:
port: 8085
servlet:
context-path: /uac即让授权中心服务启动在本地的 8085端口之上
- 创建一个带指定权限的模拟用户
@Component
public class SheepUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
if( !"codesheep".equals(s) )
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户" + s + "不存在" );
return new User( s, passwordEncoder.encode("123456"), AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_NORMAL,ROLE_MEDIUM"));
}
}这里创建了一个用户名为codesheep,密码 123456的模拟用户,并且赋予了 普通权限(ROLE_NORMAL)和 中等权限(ROLE_MEDIUM)
- 认证服务器配置
AuthorizationServerConfig
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServerConfig extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
// 定义了两个客户端应用的通行证
clients.inMemory()
.withClient("sheep1")
.secret(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"))
.authorizedGrantTypes("authorization_code", "refresh_token")
.scopes("all")
.autoApprove(false)
.and()
.withClient("sheep2")
.secret(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"))
.authorizedGrantTypes("authorization_code", "refresh_token")
.scopes("all")
.autoApprove(false);
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
endpoints.tokenStore(jwtTokenStore()).accessTokenConverter(jwtAccessTokenConverter());
DefaultTokenServices tokenServices = (DefaultTokenServices) endpoints.getDefaultAuthorizationServerTokenServices();
tokenServices.setTokenStore(endpoints.getTokenStore());
tokenServices.setSupportRefreshToken(true);
tokenServices.setClientDetailsService(endpoints.getClientDetailsService());
tokenServices.setTokenEnhancer(endpoints.getTokenEnhancer());
tokenServices.setAccessTokenValiditySeconds((int) TimeUnit.DAYS.toSeconds(1)); // 一天有效期
endpoints.tokenServices(tokenServices);
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception {
security.tokenKeyAccess("isAuthenticated()");
}
@Bean
public TokenStore jwtTokenStore() {
return new JwtTokenStore(jwtAccessTokenConverter());
}
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter jwtAccessTokenConverter(){
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey("testKey");
return converter;
}
}这里做的最重要的两件事:一是 定义了两个客户端应用的通行证(sheep1和sheep2);二是 配置 token的具体实现方式为 JWT Token。
- Spring Security安全配置
SpringSecurityConfig
@Configuration
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManager();
}
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider() {
DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
authenticationProvider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
authenticationProvider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
authenticationProvider.setHideUserNotFoundExceptions(false);
return authenticationProvider;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.requestMatchers().antMatchers("/oauth/**","/login/**","/logout/**")
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/oauth/**").authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin().permitAll();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider());
}
}客户端应用创建和配置
本文创建两个客户端应用:codesheep-client1 和codesheep-client2,由于两者类似,因此只以其一为例进行讲解
- SSO客户端应用配置类
ClientWebsecurityConfigurer
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@EnableOAuth2Sso
public class ClientWebsecurityConfigurer extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/**").authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}复杂的东西都交给注解了!
- application.yml配置
auth-server: http://localhost:8085/uac
server:
port: 8086
security:
oauth2:
client:
client-id: sheep1
client-secret: 123456
user-authorization-uri: ${auth-server}/oauth/authorize
access-token-uri: ${auth-server}/oauth/token
resource:
jwt:
key-uri: ${auth-server}/oauth/token_key这里几项配置都非常重要,都是需要和前面搭建的授权中心进行通信的
- 创建测试控制器
TestController
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/normal")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_NORMAL')")
public String normal( ) {
return "normal permission test success !!!";
}
@GetMapping("/medium")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_MEDIUM')")
public String medium() {
return "medium permission test success !!!";
}
@GetMapping("/admin")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')")
public String admin() {
return "admin permission test success !!!";
}
}此测试控制器包含三个接口,分别需要三种权限(ROLE_NORMAL、ROLE_MEDIUM、ROLE_ADMIN),待会后文会一一测试看效果
实验验证
- 启动授权认证中心
codesheep-server(启动于本地8085端口) - 启动客户端应用
codesheep-client1(启动于本地8086端口) - 启动客户端应用
codesheep-client2(启动于本地8087端口)
首先用浏览器访问客户端1 (codesheep-client1) 的测试接口:localhost:8086/normal,由于此时并没有过用户登录认证,因此会自动跳转到授权中心的登录认证页面:http://localhost:8085/uac/login:
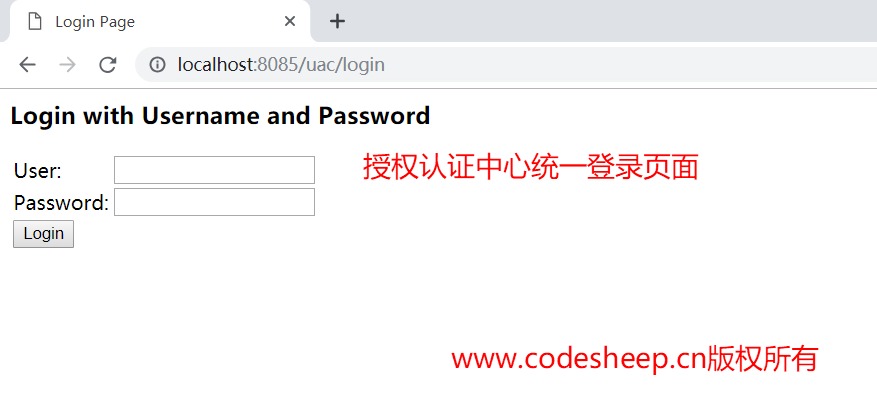
输入用户名 codesheep,密码 123456,即可登录认证,并进入授权页面:
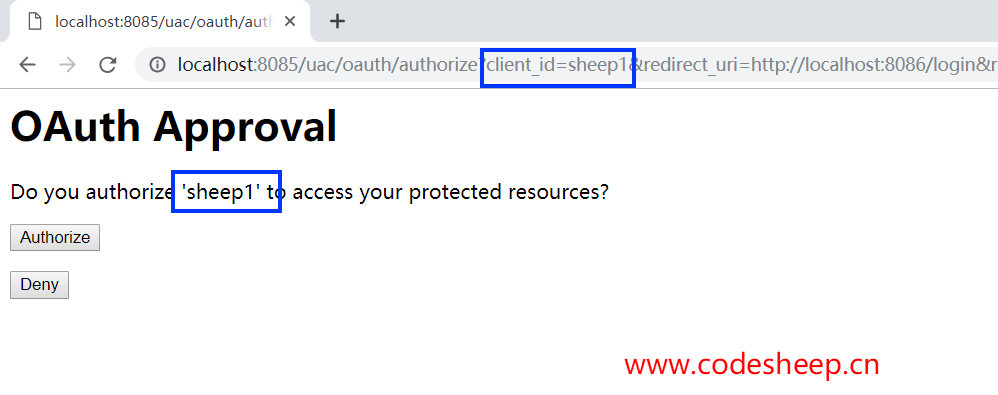
同意授权后,会自动返回之前客户端的测试接口:
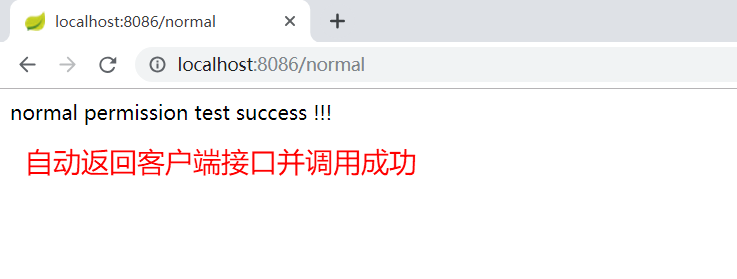
此时我们再继续访问客户端1 (codesheep-client1) 的测试接口:localhost:8086/medium,发现已经直接可以调用而无需认证了:
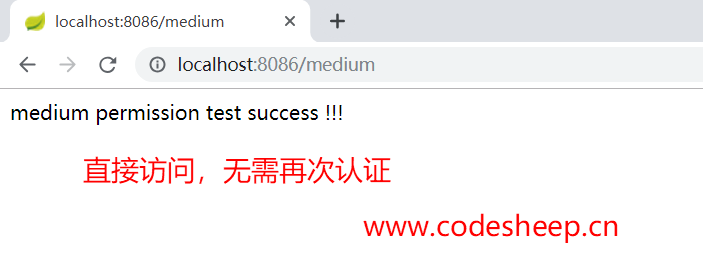
由于 localhost:8086/normal 和 localhost:8086/medium要求的接口权限,用户codesheep均具备,所以能顺利访问,接下来再访问一下更高权限的接口:localhost:8086/admin:
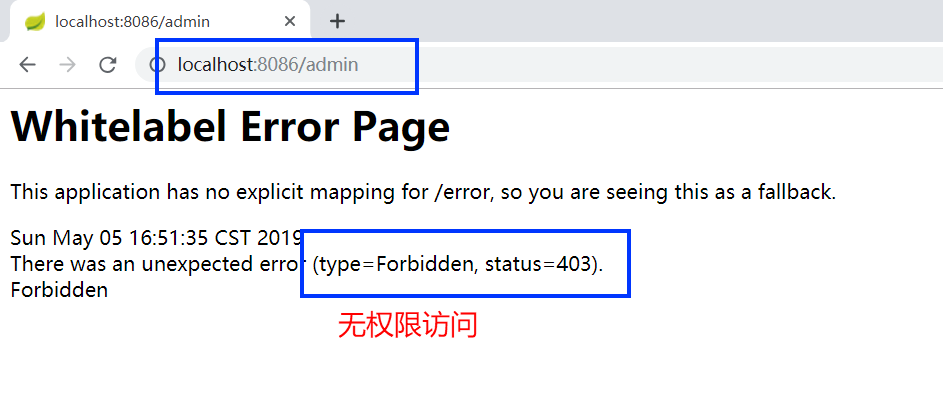
好了,访问客户端1 (codesheep-client1) 的测试接口到此为止,接下来访问外挂的客户端2 (codesheep-client2) 的测试接口:localhost:8087/normal,会发现此时会自动跳到授权页:
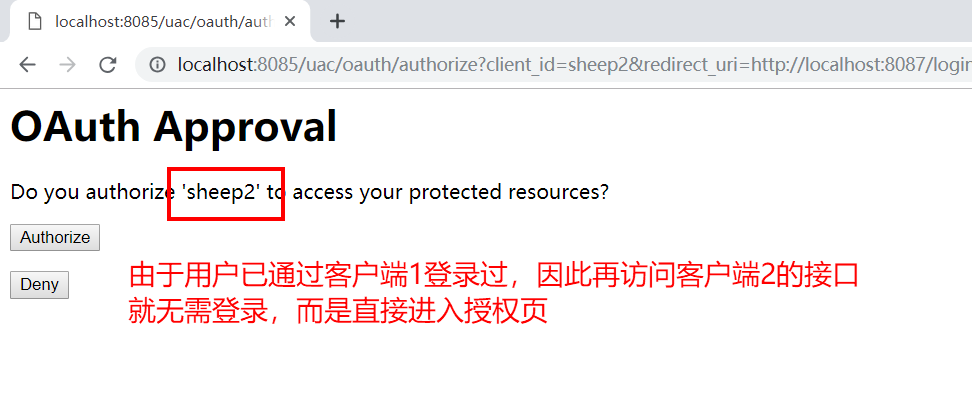
授权完成之后就可以顺利访问客户端2 (codesheep-client2) 的接口:
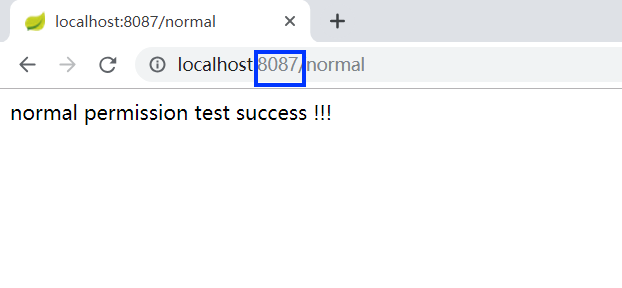
这就验证了单点登录SSO的功能了!
未完待续
受篇幅所限,本文应该说实践了一下精简流程的:SSO单点登录和JWT权限控制,还有很多可以复杂和具化的东西可以实现,比如:
- 客户端
client凭据 和 用户user的凭据可以用数据库进行统一管理 - 认证
token也可以用数据库或缓存进行统一管理 - 授权认证中心的统一登录页面可以自定义成需要的样子
- 认证中心的授权页也可以自定义,甚至可以去掉
- 包括一些异常提示也可以自定义
总之,尽情地折腾去吧!
写在最后
由于能力有限,若有错误或者不当之处,还请大家批评指正,一起学习交流!
- My Personal Blog:CodeSheep 程序羊
